Mucormycosis
• 43 year old, male presented with fever ,cough and breathing difficulty– 1 week
• Got admitted in local hospital and treated with IV antibiotics & other suppurative measures. Sputum culture showed MDR lkleibsella and got refered to Aster MIMS Kannur.
• Past history : k/c/o Type 2 DM.
• O/E – Conscious, Oriented
HR 94 , BP 70/40 ,SPO2 96%
GRBS 443, Ketones 1.8 ,Serum potassium 1.8
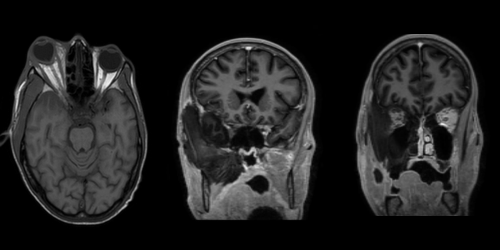
FINDINGS
• Acute infarct in right temporal lobe.
• Bulky right globe with ill defined edema, fat stranding and absent enhancement of extraocular muscles and perioptic nerve sheath in keeping with orbital cellulitis.
• Bulky right temporalis muscle, medial and lateral pterygoid muscles with ill defined edema and restricted diffusion showing loss of normal enhancement on post contrast images.
• Thrombosis of right cavernous sinus and superior ophthalmic vein.
• Acute sphenoid and right maxillary sinusitis with mucosal thickening in right ethmoidal air cells and right nasal cavity with loss of normal enhancement of right middle & inferior turbinates.
Overall features are suggestive of fungal infection – likely mucormycosis.
MUCORMYCOSIS
Mucormycosis is an uncommon but fatal fungal infection primarily affecting patients who are immunocompromised, especially those with diabetes. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for survival. The sinuses are most commonly affected, and subsequent rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis is closely associated with diabetes. A clinical presentation of orbital swelling black nasal discharge, visual defect,proptosis and headache suggests rhino-orbital-cerebral mucormycosis.
The two main named signs are Guitar pick sign and Black turbinate sign. Guitar pick sign represents conical deformation of the posteriorocular globe indicating severely increased intraorbital pressure. Black turbinate sign represents devitalized mucosa leading to a hypointense mucosal appearance on MRI.
Doctor Details:
DR SAFANA P P
PG RESIDENT,RADIOLOGY,
ASTER MIMS KANNUR
References:
• Aribandi M, McCoy VA, Bazan C 3rd. Imaging features of invasive and noninvasive fungal sinusitis: a review. Radiographics 2007; 27:1283-1296.
• Kumar J, Anbarasu A, Amarnath C, et al.. Imaging in acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis/mucormycosis. IRIA-ICRI Guidelines and Recommendations; 2021.
• Safder S, Carpenter JS, Roberts TD, et al.. The “black turbinate” sign: an early MR imaging finding of nasal mucormycosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010; 31: 771-774.
• Chikley A, Ben-Ami R, Kontoyiannis DP. Mucormycosis of the central nervous system. J Fungi (Basel) 2019; 5: 59. doi:10.3390/jof5030059.
More from AMI
Silk Vista Flow Diverter Stent – First time in Kerala @ Aster Medcity
22/11/2022
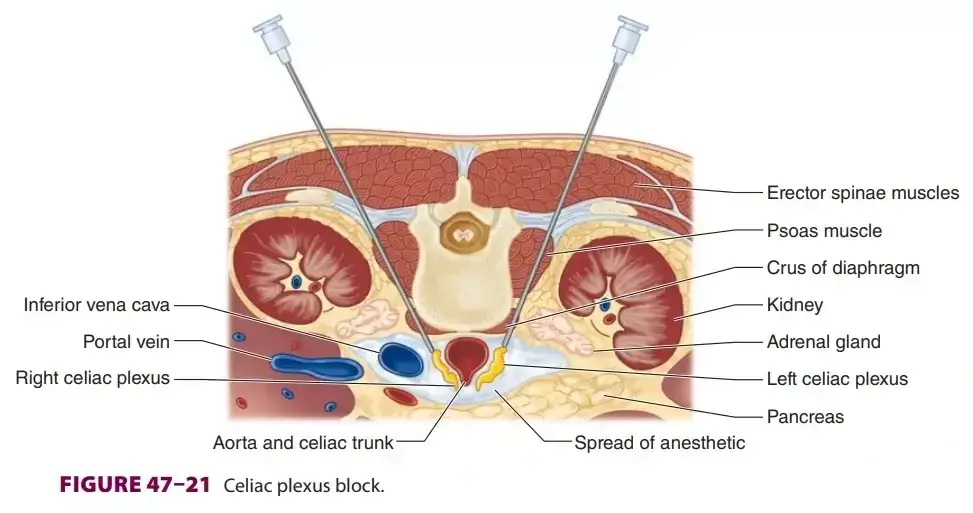
Celiac plexus block
20/12/2022
Managing Adherent Placenta – Triple Doctor’s Story.
08/12/2022
Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
17/11/2023
Call Fleming Syndrome
22/11/2022
Ectopia Cordis – A Case Study on a Rare Congenital Anomaly
29/11/2022

AMI Expertise - When You Need It, Where You Need It.
Partner With Us
